Bookkeeping
7 1 Accounts Receivable and Net Realizable Value Financial Accounting
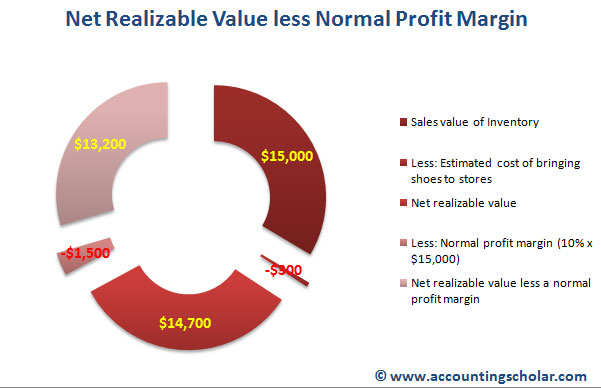
Often, a company will assess a different NRV for each product line, then aggregate the totals to arrive at a company-wide valuation. Be aware the NRV can be used for external reporting (inventory and accounts receivable) purposes as well as internal reporting (cost accounting) purposes. Companies must now use the lower cost or NRV method, which is more consistent with IFRS rules.
Net Realizable Value as part of effective credit control
As a result, companies have shifted to the LCNRV method, leveraging insights like recognizing the split-off point in production, to improve the consistency and comparability of financial statements. When the present selling price of an inventory item falls below its cost, the NRV comes into play. By reporting the inventory at its NRV, a business avoids overstating its assets on the balance sheet, which could otherwise mislead stakeholders about the company’s profitability and overall financial position. It ensures the accuracy and reliability of financial statements by preventing the overstatement of asset values. This aspect of accounting is pivotal in presenting a transparent view of a company’s financial health, which stakeholders rely on for making informed decisions. Compliance with accounting principles, such as the Lower of Cost or Market (LCM) rule, is also upheld through meticulous NRV calculations, ensuring adherence to GAAP and IFRS.
IAS 2 generally measures inventories at the lower of cost and NRV; US GAAP does not
To calculate the NRV of receivables, subtract the estimated allowance for doubtful accounts from the gross accounts receivable. For example, if gross receivables are $100,000 and doubtful accounts are $10,000, the NRV of receivables is $90,000. Cash realizable value is calculated by estimating the amount expected to be collected from accounts receivable. Subtract the allowance for doubtful accounts from the total accounts receivable.
What can Net Realizable Value tell you about your business?
Our AI-powered Anomaly Management Software helps accounting professionals identify and rectify potential ‘Errors and Omissions’ throughout the financial period so that teams can avoid the month-end rush. The AI algorithm continuously learns through a feedback loop which, in turn, reduces false anomalies. We empower accounting teams to work more efficiently, accurately, and collaboratively, enabling them to add greater value to their organizations’ accounting processes. In this blog, we will explain the concept of NRV, how to calculate it, and provide examples to illustrate its application.
- While they seem similar, there are nuanced differences between the two methods, especially post the FASB update in 2015 replacing the LCM with LCNRV in the GAAP framework.
- For example, if gross receivables are $100,000 and doubtful accounts are $10,000, the NRV of receivables is $90,000.
- Accordingly, these decommissioning and restoration costs are recognized in profit or loss when items of inventory have been sold.
- The company states that as part of its calculation of inventory, the company wrote-down $592 million.
- Just determining whether the $112 million in uncollectible accounts is a relatively high or low figure is quite significant in evaluating the efficiency of Dell’s current operations.
- A positive NRV implies that your inventory will generate profits for you, whereas a negative NRV shows that the value of your goods is lower than their cost.
Measurement of Inventory at the Lower of Cost and Net Realisable Value
As prices are elevated, the government may choose to combat rising prices. In either situation (high inflation or high unemployment), it may be more difficult for clients or businesses to find budget for additional goods to buy. As economies thrive, clients often have more money at their disposal and are able to pay higher prices. Alternatively, when the economy is down, clients may pass on orders what is meant by nonoperating revenues and gains or find it more difficult to make full payments. By submitting, you agree that KPMG LLP may process any personal information you provide pursuant to KPMG LLP’s Privacy Statement. Dual preparers should carefully assess all differences to prepare a model that is efficient to maintain, most representative of their inventory values and compliant with all applicable requirements under both GAAPs.
What are the requirements of IAS 2?
This ensures that businesses have a realistic view of their financial standing. NRV is particularly important for valuing inventory and accounts receivable. By calculating NRV, businesses can avoid overestimating the value of their assets, which enhances financial reporting accuracy and supports better decision-making. When you set out to determine the expected selling price for an asset, you’re effectively gauging its market value—the price that buyers are willing to pay under normal business conditions. It’s vital to capture a realistic figure that is neither too optimistic nor too pessimistic, aligning with the conservatism principle in accounting, which prefers understated assets and revenues over the overstatement.
Think of it as peeling back layers to reveal the core value of the asset that will actually translate into cash once the invoice amount is settled. This was updated in 2015 to where companies must now use the lower of cost or NRV method, which is more consistent with IFRS rules. In essence, the term “market” has been replaced with “net realizable value.” Knowledgeable decision makers understand that some degree of uncertainty exists with all such balances. By including this amount, company officials are asserting that they have obtained sufficient evidence to provide reasonable assurance that the amount collected will not be a materially different figure2.
First, the approach requires substantial assumptions from management about the future of the product. For goods clouded with uncertainty, it may be nearly impossible to predict obsolescence, product defects, customer returns, pricing changes, or regulation. Loosely related to obsolescence, market demand refers to customer preferences, tastes, and other influencing factors. In addition to a good becoming outdated, broad markets may be interested in substitute products, advanced products, or cheaper products. Competition always runs the risk of supplanting a good’s market position, even if both goods are still relevant and highly functioning.
